Chapter 11 Vocabulary
Genetics-Scientific study of hereditary

http://www.ornl.gov/sci/techresources/Human_Genome/genetics.shtml
True-Breeding- Organisms that produce offspring identical to themselves if allowed to self pollinate.

http://biology.about.com/bldeftruebreed.htm
Trait- Specific characteristics that varies from one individual to another.

Genetics-Scientific study of hereditary

http://www.ornl.gov/sci/techresources/Human_Genome/genetics.shtml
True-Breeding- Organisms that produce offspring identical to themselves if allowed to self pollinate.

http://biology.about.com/bldeftruebreed.htm
Trait- Specific characteristics that varies from one individual to another.

http://webspace.ship.edu/cgboer/genpsytraits.html
Hybrid- Offspring of crosses between parents with different traits.
Hybrid- Offspring of crosses between parents with different traits.

http://www.biology-online.org/dictionary/Hybrid
Gene- Sequence of DNA that codes fro a protein and thus determines a trait.

Gene- Sequence of DNA that codes fro a protein and thus determines a trait.

http://biology.about.com/od/geneticsglossary/g/alleles.htm
Segregation- Separation of alleles during gamete formation.

Segregation- Separation of alleles during gamete formation.

http://www.biology-online.org/dictionary/Gamete
Probability- Likelihood that a particular event will occur.

http://www.mathgoodies.com/lessons/toc_vol6.html
Punnett square- Diagram showing the gene combinations that might result from a genetic cross.
Probability- Likelihood that a particular event will occur.

http://www.mathgoodies.com/lessons/toc_vol6.html
Punnett square- Diagram showing the gene combinations that might result from a genetic cross.

Homozygous- Term used to refer to an organisms that has two identical alleles fro a particular trait. 

Heterozygous-Term used to refer to an organism that has two different alleles of the same trait.

Phenotype-Physical characteristics of an organism.

http://www.brooklyn.cuny.edu/bc/ahp/BioInfo/SD.Geno.HP.html
Genotype- genetic makeup of an organism

http://www.brooklyn.cuny.edu/bc/ahp/BioInfo/SD.Geno.HP.html
Genotype- genetic makeup of an organism
Homologous-Chromosomes that each have a corresponding chromosome from the opposite-sex parent

http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/homologous

http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/homologous
Diploid- A cell that contains both sets of homologous chromosomes
http://www.biology-online.org/dictionary/Diploid
 Haploid- A cell that contains only a single set of chromosomes and therefore only a single set of genes.
Haploid- A cell that contains only a single set of chromosomes and therefore only a single set of genes.Meiosis- Process by which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes in a diploid cell.
http://www.accessexcellence.org/RC/VL/GG/meiosis.html
Tetrad-Structure containing 4 chromatids that forms during meiosis.
Tetrad-Structure containing 4 chromatids that forms during meiosis.
http://answers.yahoo.com/question/index?qid=20061030200732AAJD3T4
Crossing-over- Homologous chromosomes exchange portions of their chromatids during meiosis.

Crossing-over- Homologous chromosomes exchange portions of their chromatids during meiosis.

Gene Map- Diagram showing the relative locations of each known gene on a particular chromosome.
 http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/22827585/
http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/22827585/ 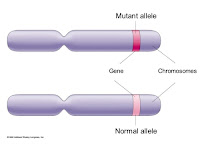




No comments:
Post a Comment